
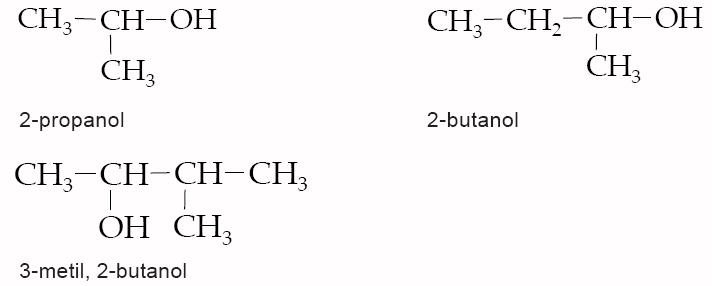
pKa NuclephilicityĪn alcohol a thiol an ether a thioether an amine an alkyne a nitrileġ-bromo-1,1-dimethylethane 1,1-dimethylethanol Rate law: rate = k this reaction is an example of a SN1 reaction.

The leaving group relative rates of reaction pKa HX HO- + RCH2I RCH2OH + I HO- + RCH2Br RCH2OH + Br HO- + RCH2Cl RCH2OH + Cl HO- + RCH2F RCH2OH + F The nucleophile In general, for halogen substitution the strongest the base the better the nucleophile. Steric effect activation energy: DG2 Energy activation energy: DG1 reaction coordinate reaction coordinate Inversion of configuration (S)-2-bromobutane (R)-2-butanol Hughes and Ingold proposed the following mechanism: Transition state Increasing the concentration of either of the reactant makes their collision more probable. The reaction of an alkyl halide in which the halogen is bonded to an asymetric center leads to the formation of only one stereoisomer When the hydrogens of bromomethane are replaced with methyl groups the reaction rate slow down. S stands for substitution N stands for nucleophilic 2 stands for bimolecularĪlkyl halide Relative rate 1200 40 1 ≈ 0 The rate of reaction depends on the concentrations of both reactants.

(1) (2) bromomethane methanol Rate law: rate = k this reaction is an example of a SN2 reaction. If concentration of (2) is doubled, the rate of the reaction is doubled. If concentration of (1) and (2) is doubled, the rate of the reaction quadruples. (1) (2) bromomethane methanol If concentration of (1) is doubled, the rate of the reaction is doubled.

Synthesized by red algae red algae Synthesized by sea hare a sea hare Substitution reaction on these compounds are easy and are used to get a wide variety of compounds alkyl fluoride alkyl chloride alkyl bromide alkyl iodide Aril Halida Dalam Pembahasan TersendiriĤ Organic compounds with an electronegative atom or an electron-withdrawing group bonded to a sp3 carbon undergo substitution or elimination reactions - Substitution Elimination Halide ions are good leaving groups. SN-2 Metil Halida Alkil halida Primer Alkil Halida Sekunder Alkil Halida Tersier Alil Halida Benzil Halida SN-2 SN-2, SN-1 dan E-2 SN-2, SN-1 dan E-2 SN-2, SN-1 SN-2, SN-1 7. Struktur (Metil, Primer, Sekunder, Tersier, Benzil dan Vinil) Reaksi (SN-2, SN-1, E-2 dan E-1) Reaction of Alkyl Halides By: Ismiyarto, MSiĢ ALKIL HALIDA Manfaat (Pestisida, Bahan Dasar Sintesis Alkohol, Alkena) Presentation on theme: "Substitution and Elimination"- Presentation transcript:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
